Pedicle Screw Fixation
Treatment > Pedicle Screw Fixation

Pedicle Screw Fixation
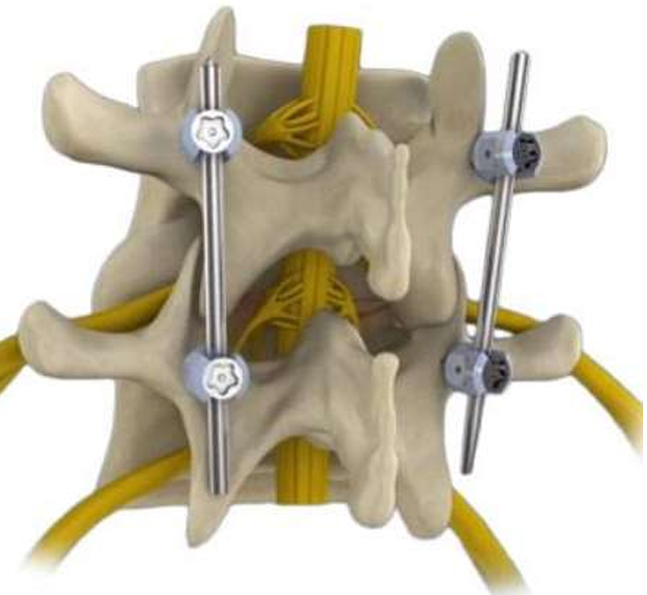
Pedicle screws are threaded titanium or stainless-steel implants that are fastened through the vertebral pedicles located at the back of the spinal bones. Pedicle screws help secure rods and/or plates to the spinal segment(s) during a spinal fusion surgery.
The screws act as anchor points and are typically positioned at 2 or 3 consecutive spinal segments connected by a short rod.
After the fusion is completely healed, the screws and rods can be removed. Removal isn’t necessary unless they cause the patient discomfort.
Who needs Pedicle screw fixation ?
Pedicle screws are used to stabilie the spinal column and achieve fusion. Patients with spinal fractures, Instability, Spondylolisthesis, spinal deformities, spine Infections, spinal tumours may need pedicle screw fixation.
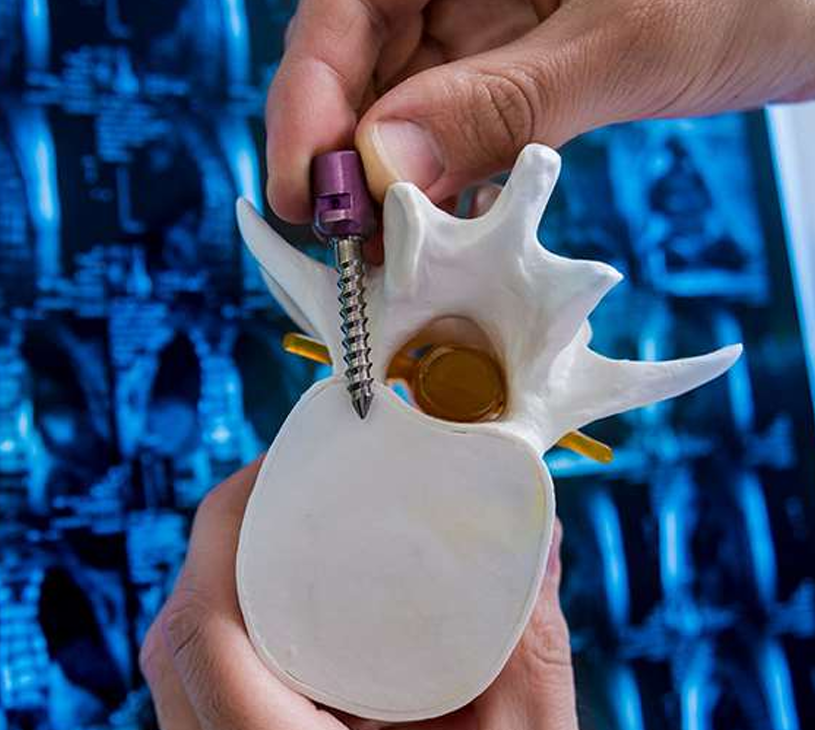
Pedicle Screw Placement
Screws may be placed using free-hand techniques 3 of screws vary and are usually determined using computed tomography (CT) scans or by computer-assisted navigation. 4 The diameter and length taken before surgery.
While imaging technology, such as fluoroscopy and computed tomography are considered to have higher accuracy in placement, the free-hand technique used by an experienced surgeon may be less likely to result in damage to the side wall of the pedicle. 5 Such damage increases the risk of injury to nearby blood vessels, such as the aorta.
Pedicle screws can also be placed via minimally invasive procedures through the skin, such as for the treatment of fractures or deformities in the spine. This type of placement is called percutaneous pedicle screw fixation.
Potential Risks and Complications of Pedicle Screw Fixation
Generally, a complication from the pedicle screw is rare, occurring in about 6% of cases. The potential complications from pedicle screws typically include a problem with the rod-screw system or an injury to the adjacent tissues.
- Screw malposition
- Dural tear
- Nerve root or Spinal cord injury
- Vascular injury
- Visceral injury
- Bleeding
- Infection