Scoliosis
Service > Scoliosis
Scoliosis
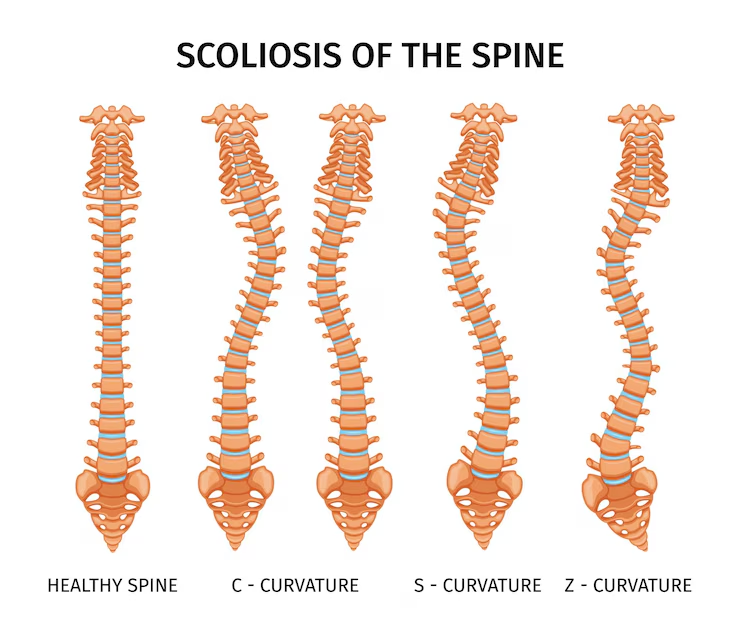
Scoliosis is a sideways curve of the spine. Everyone has normal curves in the spine, and when looked at from behind, the spine appears straight. However, children and teens with scoliosis have an abnormal S shaped or C-shaped curve of the spine. The curve can happen on either side of the spine and in different places in the spine. In most people, the cause of scoliosis is unknown.
Other causes could be Congenital (Birth defect), neuromuscular or syndromic. Scoliosis is diagnosed by examining your child or teen and taking x-rays. This helps to develop a treatment plan, which depends on the location and severity of the curve. Children and teens with milder curves may just need observation and bracing.
Curves which are severe, progressing fast, causing
pain or cosmetic or lung or neurological problems
needs surgical correction of scoliosis
🔷 Scoliosis – Background
Scoliosis is a condition where the spine curves abnormally to the side, forming an “S” or “C” shape. While mild curves may not cause major issues, moderate to severe scoliosis can lead to pain, uneven posture, breathing difficulties, and in some cases, visible spinal deformity. It can develop in children during growth (adolescent idiopathic scoliosis) or in adults due to spinal degeneration or other causes.
📌 Common Causes:
Idiopathic scoliosis (unknown cause, common in teenagers)
Congenital spinal deformities (present at birth)
Neuromuscular conditions (e.g., cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy)
Degenerative spine diseases in adults
Spinal injuries or infections
📌 Typical Symptoms:
Uneven shoulders, waist, or hips
One shoulder blade more prominent than the other
Visible curvature of the spine
Back pain or discomfort
Difficulty standing straight or wearing clothes evenly
In severe cases, breathing issues due to reduced lung space
📌 Why Early Treatment Is Essential:
Detecting scoliosis early, especially in children, can help manage the condition before it progresses. Timely treatment can prevent complications, improve posture, and in many cases, avoid the need for surgery.
📌 Available Services May Include:
Clinical assessment and spinal examination
X-rays or advanced imaging for curve measurement
Monitoring and regular follow-up for mild cases
Bracing (especially in growing children to stop curve progression)
Physical therapy to strengthen back muscles and improve posture
Surgical correction (spinal fusion or advanced techniques) for severe curves
Post-treatment rehabilitation and long-term monitoring

